What's in this article?
What is an allergy?
An allergy is a reaction by your immune system to something that does not bother most other people. People who have allergies often are sensitive to more than one thing. Substances that often cause reactions are
- Pollen
- Dust mites
- Mold spores
- Pet dander
- Food
- Insect stings
- Medicines
Normally, your immune system fights germs. It is your body’s defense system. In most allergic reactions, however, it is responding to a false alarm. Genes and the environment probably both play a role.
Allergies can cause a variety of symptoms such as a runny nose, sneezing, itching, rashes, swelling, or asthma. Allergies can range from minor to severe. Anaphylaxis is a severe reaction that can be life-threatening. Doctors use skin and blood tests to diagnose allergies. Treatments include medicines, allergy shots, and avoiding the substances that cause the reactions.
Allergy facts
- Allergy involves an exaggerated response of the immune system, often to common substances such as foods or pollen.
- The immune system is an intricate system that defends the body against foreign invaders, such as bacteria and viruses, while also surveying for conditions such as cancer and autoimmunity.
- Allergens are substances that are foreign to the body and can cause an allergic reaction.
- IgE is the allergic antibody.
- Allergies can not only develop at any age, but many individuals also outgrow allergies over time.
- A person has a greater risk of developing allergic conditions if there is a family history of allergy, especially in their parents or siblings, but the environment also plays a role.
Symptoms
Allergy symptoms depend on the substance involved and can involve the airways, sinuses and nasal passages, skin, and digestive system. Allergic reactions can range from mild to severe. In some severe cases, allergies can trigger a life-threatening reaction known as anaphylaxis.
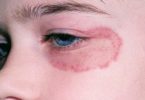
Hay fever, also called allergic rhinitis, may cause:
- Sneezing
- Itching of the nose, eyes or roof of the mouth
- Runny, stuffy nose
- Watery, red or swollen eyes (conjunctivitis)
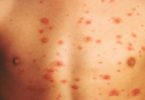
A food allergy may cause:
- Tingling mouth
- Swelling of the lips, tongue, face or throat
- Hives
- Anaphylaxis
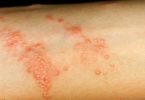
An insect sting allergy may cause:
- A large area of swelling (edema) at the sting site
- Itching or hives all over your body
- Cough, chest tightness, wheezing or shortness of breath
- Anaphylaxis
A drug allergy may cause:
- Hives
- Itchy skin
- Rash
- Facial swelling
- Wheezing
- Anaphylaxis
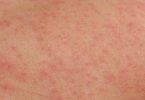
Atopic dermatitis, an allergic skin condition also called eczema, may cause skin to:
- Itch
- Redden
- Flake or peel
Allergy Treatment
There are lots of allergy treatment options. Over-the-counter and prescription medications can ease annoying symptoms. Allergy shots also help.
- Antihistamines
When medicine is needed to stem allergy symptoms, antihistamines are often first in line. Find out how they can help and learn about possible side effects. - Decongestants
Learn how decongestants work – and who should not use them. - Anticholinergic Nasal Allergy Sprays
Atrovent nasal spray can help with certain allergy symptoms. Find out if it’s right for you. - Steroid Nasal Sprays
Steroid nasal sprays are one of the strongest allergy medications. Find out how they work and how to use them. - Allergy Eye Drops
Find out when allergy eye drops can help and who should not use them. - Leukotriene Inhibitors
These medications are fairly new to the allergy world. Find out if they’re right for you. - Mast Cell Inhibitors
This type of medication can help but it’s all in the timing. Find out how to use it for best results. - Allergy Shots
For some people, allergy shots can mean the end to allergy medication. Find out all you need to know. - Skin Allergies
Advanced Reading: This article, written for doctors, provides in-depth information on skin allergy treatments. - Dehumidifiers for Allergies
If mold, mildew, or dust mite allergies are making you miserable, a home dehumidifier may help. - When to Use Your Auto-Injector
An auto-injector such as EpiPen, Twinject, or Auvi-Q can treat extreme allergic reactions with an early, life-saving dose of epinephrine.