What's in this article?
Fungal infections are contagious and can spread from one person to another. But humans do have protections against fungi. For one, almost every part of the human body has non-disease causing bacteria that protect us from fungal infections.
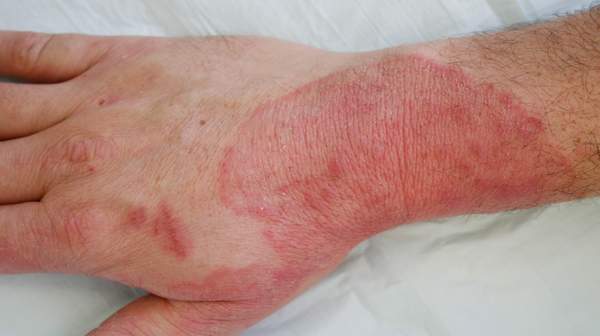
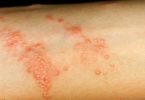
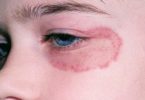
Scalp ringworm is found on the head, and body ringworm affects any other skin areas. Athlete’s foot is another type of fungal infection that usually appears between the toes but can also affect toenails and the bottom or sides of the feet. Jock itch is a fungal infection of the groin and upper thighs.
These bacteria deprive harmful fungi of space and nutrients, thereby keeping them in check. Secondly, even if fungi do manage to colonize the skin, the body’s immune system can often fight them off. High acidity levels in some environments such as the vagina provide another layer of protection.
Types of Fungal skin infections:
- Athlete’s Foot
- Jock Itch
- Ringworm
- Onychomycosis
- Candidiasis Albicans
- Athlete’s foot (Tinea pedis)
- Nail infections (Tinea unguium)
- Ringworm of the body (Tinea corporis)
- Ringworm of the groin (Tinea cruris)
- Ringworm of the scalp (Tinea capitis)
- Yeast infections
- Intertrigo
- Pityriasis versicolor (Tinea versicolor)
- Thrush (Candida albicans)
- Other Opportunistic Organisms
Symptoms of fungal skin infections
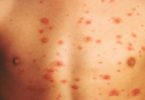
The symptoms and appearance of a fungal skin infection depend on the type of fungus that has caused it. They will also depend on which part of your body is affected. Fungal rashes are sometimes confused with other skin conditions, such as psoriasis and eczema.
Fungal skin infections can cause a variety of different skin rashes. Some are red, scaly and itchy. Others may produce a fine scale, similar to dry skin. The fungus can affect just one area, or several areas of your body. If you get a fungal infection of your scalp, you may lose some hair.
Treatment and Medicines
You will usually need to use an antifungal treatment that you put directly onto the affected area of your skin. These are known as topical treatments. There are a variety of treatments available in the form of creams, lotions, paints, shampoos and medicated powders. Some of these are available over the counter from a pharmacist, without prescription. Always read the patient information leaflet that comes with your medicine and if you have any questions, ask your pharmacist for advice.
If you have a rash that covers a large area of your skin or affects your nails or scalp, you may need to take tablets. Your GP may also prescribe you tablets if you have used a topical treatment that hasn’t worked. These treatments can occasionally cause side-effects, which include skin irritation and stomach problems.
How Can Fungal Infections Be Prevented?
Many patients develop fungal infections when they are being treated for another disorder, and their immune system is compromised. Make sure to consult with a healthcare provider. It also helps to avoid the prolonged usage of steroids or antibiotics.
Good hygiene is critical for avoiding fungal infections. Some specific tips:
- Keep the skin, especially the folds of the skin, clean and dry.
- Wash hands often, especially after touching animals or other people.
- Avoid using other people’s towels.
- Wear shoes in community showers and swimming pools.
- Wipe gym equipment before and after use.