What's in this article?
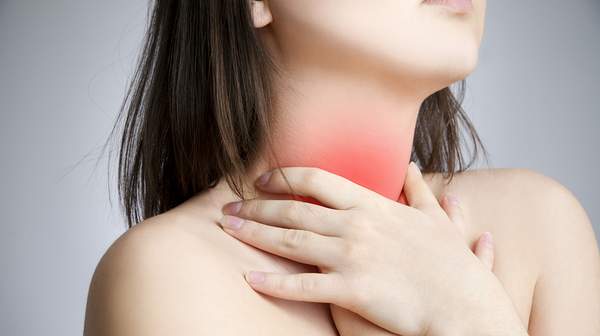
A sore throat (pharyngitis) is normally a symptom of a bacterial or viral infection, such as the common cold. In around a third of cases, no cause for the sore throat can be found.
If you have a sore throat, you may also have:
- swollen tonsils (tonsillitis)
- enlarged and tender glands in your neck
- discomfort when swallowing
If your sore throat is caused by bacteria or a virus, you may also experience symptoms associated with common infectious conditions, such as:
- a high temperature (fever) of 38C (100.4F) or over
- aching muscles or tiredness
- a headache
- a cough
- a runny nose
Sore Throat Causes
There are several causes of a sore throat.
Viral Infection
The majority of sore throats are triggered by a viral infection. These are infections caused by a virus, such as the cold and flu.
Other types of viral infections include:
- mononucleosis: infectious disease typically transmitted through saliva
- measles: contagious illnesses characterized by a distinct rash and fever
- chickenpox: infection that causes skin sores
- croup: infection of the larynx
Bacterial Infection
A bacterial infection can also cause a sore throat. These types of infections include:
- strep throat: inflammation of the throat caused by theStreptococcal bacteria
- diphtheria: infectious disease that causes throat inflammation
- whooping cough: disease of the respiratory mucous membrane
Environmental Factors
Not all sore throats are viral or bacterial. There are several other causes of throat pain. If you’re allergic to mold, pet dander, pollen, or other irritants, exposure to these allergens can trigger post-nasal drip. This is when excess mucus accumulates in the back of your throat. This accumulation can irritate your throat and cause pain or inflammation.
Dry air can also make your throat feel raw and scratchy. Smoking cigarettes or exposure to cigarette smoke can trigger persistent sore throats, as well as throat strain from yelling or too much talking.
GERD
Gastroesophageal reflux disease may also cause your sore throat. This is a digestive condition characterized by the back flow of stomach acid into the esophagus. This condition causes an array of symptoms, such as a sore throat, hoarseness, heartburn, and nausea.
Sore Throat Symptoms
The signs and symptoms of a sore throat vary depending on the underlying cause. However, the common symptom shared by individuals with a sore throat is the feeling of throat pain and discomfort, which is often worsened by swallowing or talking. Some people may complain of a scratchy or dry sensation in their throat as well.
Because most cases of sore throat are caused by an infection, individuals may commonly experience any of the additional following signs and symptoms:
- Fever and chills
- Nausea and vomiting
- Body aches
- Headache
- Cough
- Runny nose or nasal congestion
- Earache
- Sneezing
- Weakness
- Lack of appetite
- Redness and/or swelling of the tonsils and back of the throat
- White patchy areas on the tonsils (exudate)
- Swollen and/or tender lymph nodes in the neck
- A muffled or hoarse voice
Distinguishing between a sore throat caused by a virus and strep throat can be challenging, but there are certain features that can often help differentiate them. Generally speaking, individuals with strep throat will have red swollen tonsils with white patches (exudate), fever, and swollen tender lymph nodes in the neck WITHOUT the symptoms typically seen with a viral infection (a “cold”) such as cough, runny nose, nasal congestion, and sneezing. However, this distinction is not always present, and therefore an evaluation with a health care professional may be necessary to accurately confirm the diagnosis. Only a throat culture (swab taken from the back of the throat) can definitively diagnose a strep throat.
Sore Throat Home Remedies
If you or someone in your family has a sore throat, the tips below may help relieve the symptoms:
- avoid food or drink that is too hot, as this could irritate the throat
- eat cool, soft food and drink cool or warm liquids
- adults and older children can suck lozenges, hard sweets, ice cubes or ice lollies
- avoid smoking and smoky environments
- regularly gargling with a mouthwash of warm, salty water may help reduce swelling or pain
- drink enough fluids, especially if you have a fever
Steam inhalation is not recommended, as it’s unlikely to help a sore throat and there is a risk of scalding.
Sore Throat Treatment
A sore throat caused by viral infection the most common cause usually lasts five to seven days and doesn’t require medical treatment.
Treating bacterial infections
If your sore throat is caused by a bacterial infection, your doctor will prescribe a course of antibiotics. Penicillin taken by mouth for 10 days is the most common antibiotic treatment prescribed for infections such as strep throat. If you’re allergic to penicillin, your doctor will prescribe an alternative antibiotic.
You must take the full course of antibiotics as prescribed even if the symptoms go away completely. Failure to take all of the medication as directed may result in the infection worsening or spreading to other parts of the body. Not completing the full course of antibiotics to treat strep throat can, in particular, increase a child’s risk of rheumatic fever and serious kidney inflammation.
Talk to your doctor or pharmacist about what to do if you forget to take a dose.
Other treatments
If a sore throat is a symptom of a condition other than a viral or bacterial infection, other treatments will likely be considered depending on the diagnosis.